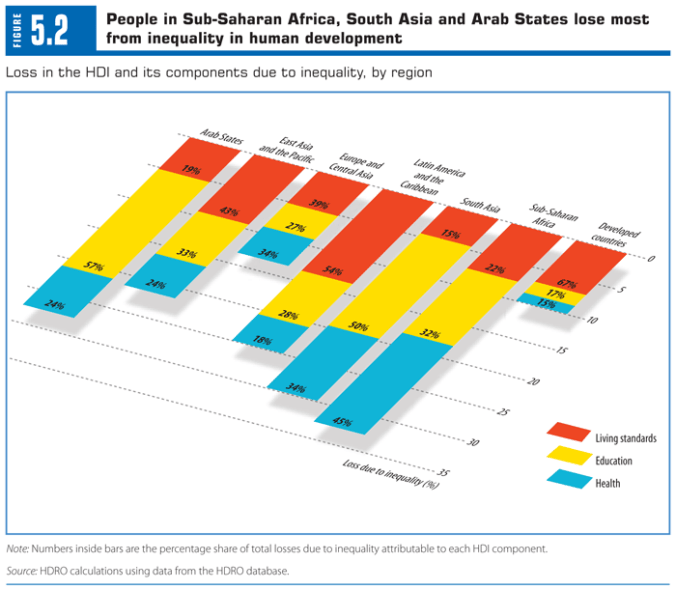
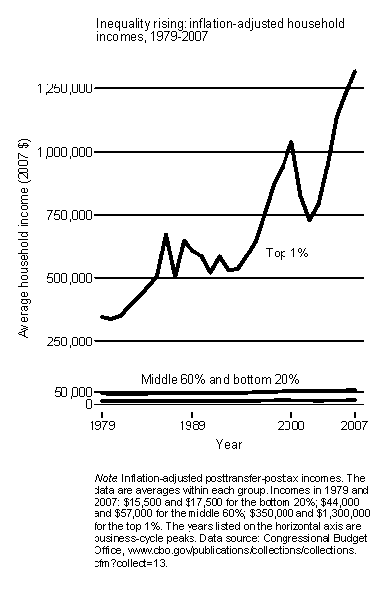
A post from Roberto Roccu.
Of course it is. Yet, Colin Hay hits the right note when he points out that if crises are conceived as moments of radical questioning and change of existing paradigms, then what we see today is not a crisis, but rather a “catastrophic equilibrium”. Indeed, now that the reverberations of the rhetoric of London’s G20 in April 2009 have faded, it appears that the measures adopted both on a national and on the global scale are concerned with shoring up the old growth model based on flexible accumulation, in the attempt to restore its economic profitability, regardless of its social unsustainability.
Rather than downplaying the magnitude of the economic problems we face, Hay’s aim is to show how in a period when all the material conditions for speaking in terms of a crisis are present, with all the potential implications for a radical reconfiguration of our economic policies and political economies, the ideational discourse is still dominated by the very paradigm that created such material conditions. This fits well with Hay’s account of the genesis of neoliberalism, which emerged as the solution to a discursively-boosted epochal crisis of Keynesianism in times where material conditions were far from being as severe as the ones we face today.
It would be easy to dismiss Hay for “being too academic”, particularly in a context where what he calls the pathologies of the neoliberal paradigm have infected all of the developed world with very real consequences for those individuals and groups that have lost their jobs and are experiencing a dramatic increase in their social insecurity. Still, identifying the distinction between existing material conditions and the missing narrative for linking those conditions and framing a coherent and credible political project is extremely fruitful. This is the hiatus where capitalist realism as an ideology and a practice has prospered. In this respect, the regained profitability of the capital accumulation regime has brought about two seemingly parallel yet interrelated trends, that are most visible in the developed country struck hardest by the crisis, the US.
On the one hand, the rise of the Tea Party movement. The mainstream press has set its focus on the populist, anti-intellectual and anti-establishment aspects of the phenomenon. Yet, their fundamentalist neoliberalism – best expressed in the call to “return to the principles of Austrian economics” – has largely gone unnoticed. On the other hand, the ever clearer and stronger political position taken by Murdoch’s media empire against the Obama administration and more generally against any kind of state intervention in the economy is equally relevant. The daily space granted to Glenn Beck on Fox appears to me as the most evident trait d’union between these two trends.
On this side of the Atlantic, dismissing these phenomena as something alien would be misleading and dangerous. And not only because Murdoch’s empire extends well within Europe, and he is even now launching an offensive on the British media. Most importantly from a social standpoint, is the other trend – the rise of populist, worryingly xenophobic yet economically conventional movements – which is manifesting itself with a surprising regularity, even in countries like Sweden, that our diehard clichés still like to characterise as “welfare paradises”.
The analysis of what is happening in the European space is rendered more complex by the presence of a further level of decision-making, located on a larger spatial scale than the state. Now, all of us have become accustomed to hear about the democratic deficit within the EU. One of its major consequences is that the struggle for influence does not follow institutionalised forms, and lobbying is by and large the name of the game. Within this context, the effective mobility and mobilisation of capital and of its allies on the EU scale (and beyond) confronts a mobility of labour that remains mostly on paper, as the bulk of the jobs that are neither highly skilled nor unskilled are still largely allocated on a national basis. As a consequence, it has proven incredibly hard to mobilise working forces beyond the national scale.
Even the rampant xenophobia – exemplified by the rise of parties such as the Northern League in Italy, the Freedom Party in the Netherlands, the Swedish Democrats in Sweden, and the list could go on to include at the least fifteen of the EU’s twenty-seven members – must be seen as a fragment that begs for relations with the whole. And in the Europe of the four freedoms of movement (people, goods, services, capital), where the mobilisation of capital is effectively globalised and the mobilisation of labour is still limited by national boundaries, it comes as no surprise that the genuine anger of the working class(es) is channelled towards an attack of the only one freedom that can credibly be limited by national authorities: the movement of people.
And yet, there would be plenty of material to start from in the direction of some Europe-wide coordination. From the Spanish general strike to the recent demonstrations in the Netherlands to industrial action on the London Underground to the French general strike of this Tuesday. Unfortunately, very little has been happening on the European scale. And as long as capital is more powerful to begin with and better organised on a larger scale whereas labour is weaker and sometimes divided also on the national scale, the prospects for resisting, reversing and subverting the current neoliberal offensive appear to be dire indeed.
 In amongst a typically judicious review of Treasure Islands and Winner-Take-All Politics, David Runciman draws a suggestive comparison between the contemporary politics of financial ‘mobility’ and the legacy of colonialism.
In amongst a typically judicious review of Treasure Islands and Winner-Take-All Politics, David Runciman draws a suggestive comparison between the contemporary politics of financial ‘mobility’ and the legacy of colonialism.