Hot on Roberto’s heels, and the third of us to achieve doctorhood since the inception of The Disorder Of Things, our very own Meera today survived the critical questioning of Robbie Shilliam and Christopher Cramer. She is henceforth Dr Sabaratnam, certified by virtue of her thesis: Re-Thinking the Liberal Peace: Anti-Colonial Thought and Post-War Intervention in Mozambique. For the record, I’m assured that any violence inflicted was purely intellectual.
Development
Human Rights Contested – Part II
This is a continuation of my previous post…
Who Are Human Rights For?
All of the authors take account of the ambiguous history of human rights, in which they can be said to have inspired the Haitian, American and French revolutions, while also justifying the counterrevolutionary post-Cold War order dominated by the United States. Yet recognising this ambiguity without also acknowledging the distinctive reconstruction of contemporary human rights that makes them part of a neo-liberal international order and the unequal power that makes such a quasi-imperial order possible would be irresponsible. A primary contribution made collectively by these texts is that they clearly diagnose the way human rights have been used to consolidate a particular form of political and economic order while undercutting the need for, much less justification of, revolutionary violence. Williams says of Amnesty International’s prisoners of conscience, who serve as archetypal victims of human rights abuse,
the prisoner of conscience, through its restrictive conditions, performs a critical diminution of what constitutes “the political.” The concept not only works to banish from recognition those who resort to or advocate violence, but at the same time it works to efface the very historical conditions that might come to serve as justifications – political and moral – for the taking up of arms.
Human rights, then, are for the civilised victims of the world, those abused by excessive state power, by anomalous states that have not been liberalised – they are not for dangerous radicals seeking to upset the social order.
Book launch: A Liberal Peace?
Tuesday 14th February 2012, 5.30pm-7.00pm
Westminster Forum, 5th Floor, Department of Politics and International Relations, University of Westminster, 32-38 Wells Street, London W1 (nearest tube Oxford Circus)
Panel with Editors David Chandler and Meera Sabaratnam, followed by publisher’s reception

The 1990s was a weird decade for all kinds of reasons. The dice that were thrown into the air as the Soviet Union retreated landed in a particularly intriguing configuration for those politicians, public functionaries and academics from wealthy countries and institutions concerned with ‘peace’ and ‘development’. Their missions, marginalised for decades under concerns for national (i.e. military) security, were quite suddenly elevated as symbols of the new world order and installed as defining foreign policy priorities of wealthy states. Continue reading
Atrocity Porn, the Resource Curse and Badvocacy in ‘Unwatchable’ (2011)
Lest it need saying, *trigger warning*.
 Unwatchable lasts just over 6 minutes, but is intended to linger far longer. A project of Save The Congo, it was apparently turned down by larger charities on the grounds that it was too extreme. Deploying liberal doses of slo-mo and orchestral overture, it shows an armed assault on a whiter-than-white (and blonder-than-blonde) family somewhere in rural England. The teenage daughter is gang-raped on the kitchen table while her father is forced to watch, and her parents are eventually mutilated and killed on their front lawn while the soldiers laugh and film them on mobile phones. At one point we see a soldier cowering to avoid the scenes wrought by his comrades. The youngest daughter is killed trying to escape. In other words, a BBFC 18-rated piece of atrocity porn doubling as a viral advocacy campaign.
Unwatchable lasts just over 6 minutes, but is intended to linger far longer. A project of Save The Congo, it was apparently turned down by larger charities on the grounds that it was too extreme. Deploying liberal doses of slo-mo and orchestral overture, it shows an armed assault on a whiter-than-white (and blonder-than-blonde) family somewhere in rural England. The teenage daughter is gang-raped on the kitchen table while her father is forced to watch, and her parents are eventually mutilated and killed on their front lawn while the soldiers laugh and film them on mobile phones. At one point we see a soldier cowering to avoid the scenes wrought by his comrades. The youngest daughter is killed trying to escape. In other words, a BBFC 18-rated piece of atrocity porn doubling as a viral advocacy campaign.
A small clickable box sits screen top-right throughout. It reads: ‘Make It Stop’. The tagline: ‘Warning: this film contains sexualised violence you and your mobile phone manufacturer may find disturbing’. The pay off being that this is really about the DRC, but that it will take this happening to white people for you to notice. Yes, this is another campaign about the resource curse and another entry in the catalogue of rape atrocity ratcheting, now with the obligatory twitter hashtag (#bloodminerals) and a petition demanding: a) that EU companies be forced into transparent supply chains for coltan and the like; and b) that ‘swift and severe’ action be taken against any party responsible for violence.
Kate at Wronging Rights picks up on the incoherence of Save the Congo’s accompanying claims:
W…T…F…? Rape is cheaper and much more effective than guns or bullets??? No. Rape is not a “cheap” coercive strategy. It’s time-consuming and it exposes the perpetrators to injury and potential STD infection. Armed groups absolutely use it anyway, but not because it’s cheaper than bullets.
And, [i]f armed groups were to raid a village and force the population to leave by shooting at them, NGOs could be alerted and the UN would have to react?? This is surely news to the scores of NGOs, both local and international, who have worked tirelessly to document and publicize the use of rape as a weapon of war throughout the last decade and a half of conflict in the region.
Look, I realize that grassroots activism often plays a fundamental role in political change, and has been particularly important to the history of the human rights movement, but seriously, this “the news made me sad / I can haz NGO?” nonsense has got to stop. Time to invoke Amanda’s “Love Actually Test” on a wider scale, I think.
Bizarre and untenable as such ideas may be (say what?), the key points of Save the Congo’s analysis are ones now commonly repeated as part of the general ‘weapon of war’ narrative. Continue reading
Looking Beyond Spring for the Season: Echoes of Time Before Tahrir Square
This is the fifth and last part in a series of posts from Siba Grovogui, Professor of International Relations and Political Theory at John Hopkins University. The first part is here; the second here; the third here; the fourth here. The series considers the character and dimensions of the tension between the African Union and ‘the West’ over interventions in Africa. As before, responsibility for visuals adheres solely to Pablo K.
 It would be disingenuous to relate events in North Africa and the Middle East (or MENA) today without reference to the media. Here too, there are many possible angles to examine. I will focus on the institutional support that the media provide in shaping consensus in support of foreign policy. In this regard, so-called mainstream Western media and networks (BBC, CNN, Fox, RFI and the like) have played a significant role in generating domestic support for the Libyan campaign. The media find themselves in the contradictory positions of both providing sustenance to foreign policy rationales and reporting on government actions. In this role the media either wittingly or unwittingly assumed the position of justifying contradictory Western foreign policy aims while trying to satisfy the needs of their audiences (especially domestic constituencies and home governments) for information from the front. Consistently, the media often generate sympathy for foreign actors or entities that either support Western interests or have affinities for Western values.
It would be disingenuous to relate events in North Africa and the Middle East (or MENA) today without reference to the media. Here too, there are many possible angles to examine. I will focus on the institutional support that the media provide in shaping consensus in support of foreign policy. In this regard, so-called mainstream Western media and networks (BBC, CNN, Fox, RFI and the like) have played a significant role in generating domestic support for the Libyan campaign. The media find themselves in the contradictory positions of both providing sustenance to foreign policy rationales and reporting on government actions. In this role the media either wittingly or unwittingly assumed the position of justifying contradictory Western foreign policy aims while trying to satisfy the needs of their audiences (especially domestic constituencies and home governments) for information from the front. Consistently, the media often generate sympathy for foreign actors or entities that either support Western interests or have affinities for Western values.
This role is not without a cost, especially when foreign policy actions, including wars, fail to attain their objectives. When the outcome of foreign policy proves disastrous, Western media also have an inexhaustible capacity to either ignore their prior support for the underlying causes or to reposition themselves as mere commentators on events over which they had no control or could not prevent. Increasingly, these tendencies have spread around the world as evidenced in the techniques and styles that have propelled the Qatari-based Al Jazeera into prominence as key contender in the emergent game of production, circulation, and consumption of foreign policy-concordant images for their affective and ideological effects.
So it is not surprising that the backdrop and background scenarios for most reporting on the 2011 revolts in MENA are dimensions of Orientalism, of which they are many. But the most constant is one of autocratic ‘barbarism’. In this regard, the discourses and media techniques for creating and supporting sympathetic figures are just as constant (or invariable) as Western states rationales for intervention. The media-hyped stories of Oriental despotism that preceded Operation Desert Storm, when the US expelled Iraq from Kuwait, have provided the template. During that event, for instance, media feted their viewers with stories of invading Iraqi hordes storming through hospital only to disconnect incubators and let helpless infants die a slow death. These and many stories of heroic bids by US soldiers to prevent such barbarism were later discredited but not the other horrific stories which convinced US citizens of the need to wage war on Saddam Hussein’s occupying army. In the Libyan case today, one of the earlier images of the aura of impunity created by Gaddafi was that of a Libyan female lawyer who was allegedly raped by Gaddafi’s forces. There was also a reported event of military takeover of a hospital.
Looking Beyond Spring for the Season: Democratic and Non-Democratic Cultures
This is the fourth part in a series of five posts from Siba Grovogui, Professor of International Relations and Political Theory at John Hopkins University. The first part is here; the second here; the third here. The series considers the character and dimensions of the tension between the African Union and ‘the West’ over interventions in Africa. As before, responsibility for visuals adheres solely to Pablo K.
 It is not accurate to say that the African Union has been indifferent to the conflict in Libya. If there has been silence in Africa, it has to do with the extent to which the ‘maverick’ Colonel (Gaddafi) has angered some of his peers over the years by interfering in the affairs of such states as Nigeria, Liberia, Burkina Faso, Sierra Leone and others, with disastrous effects. Even when, as in Sudan and Uganda, officeholders have welcomed his entreaties, large segments of the populations have not appreciated them. Yet, regardless of their personal views of Gaddafi and their political differences with him, African elites and populations have yearned for a more positive, conciliatory, and participatory solution to outright regime change or the removal of Gaddafi preferred by the West. This variance, I surmise, comes from a positive understanding of postcoloniality that include forgiveness, solidarity, and democracy and justice, as exhibited in post-apartheid South Africa and post-conflict Liberia, Angola, Mozambique, and the like.
It is not accurate to say that the African Union has been indifferent to the conflict in Libya. If there has been silence in Africa, it has to do with the extent to which the ‘maverick’ Colonel (Gaddafi) has angered some of his peers over the years by interfering in the affairs of such states as Nigeria, Liberia, Burkina Faso, Sierra Leone and others, with disastrous effects. Even when, as in Sudan and Uganda, officeholders have welcomed his entreaties, large segments of the populations have not appreciated them. Yet, regardless of their personal views of Gaddafi and their political differences with him, African elites and populations have yearned for a more positive, conciliatory, and participatory solution to outright regime change or the removal of Gaddafi preferred by the West. This variance, I surmise, comes from a positive understanding of postcoloniality that include forgiveness, solidarity, and democracy and justice, as exhibited in post-apartheid South Africa and post-conflict Liberia, Angola, Mozambique, and the like.
In opting for negotiated mediation and a new constitutional compact, therefore, the African Union (or AU) aimed to foster a different kind of politics in Libya – admittedly one that has escaped many of the states endorsing that position. As articulated by Jean Ping, the Secretary General of the AU, the Libyan crisis offered an opportunity “to enhance a self-nourishing relationship between authority, accountability and responsibility” in order to “reconstitute African politics from being a zero sum to a positive sum game” toward one “characterized by reciprocal behavior and legitimate relations between the governors and the governed.” Mr. Ping added two other dimensions to his vision. The first is an acknowledgement that events in Libya point to the fact that all Africans “yearn for liberty and equality’ and this yearning is “something more consequential than big and strong men.” The second is that Africa’s destiny should be shaped by Africans themselves based on an actualized “sense of common identity based, not on the narrow lenses of state, race or religion, but constructed on Africa’s belief in democracy, good governance and unity as the most viable option to mediate, reconcile and accommodate our individual and collective interests.”
Coming from a politician, these words may read like slogans. But the uniform refusal of the AU to endorse Western intervention tells another story. Continue reading
A Kind Of Blank Spot
[M]y wife and I realized you cannot pay attention to everything, so I said to myself “one continent that I am going to leave aside is Africa.” I preferred to concentrate on Europe and China. I did a pretty good deal of work on China because I saw it ripe to become one of the most important parts of the world of which I knew nothing. So, I proceeded to do a lot of work on China in order to know something about it. But Africa is kind of a blank spot for me, apart from casual observation. Even though, I would say that the whole notion of anarchy applies very well to Africa.
In fact, a criticism people used to make to me was that Africa was clearly an anarchic arena, and yet African states did not fight much among themselves. How, then, would a Realist like myself explain that? Well, I did by invoking Turney-High’s book in anthropology, which was published—I believe—in the 1920s. There, he made the very valid point that countries have to obtain a certain level of self-consciousness as being a political entity, and a certain level of competence before they are able to fight one another. Turney-High’s illustration was very clear with his study of the peoples he referred to as the “Californians,” who were such a primitive people that they did not have the ability to form groups or fight as a group. A consciousness and competence at a certain level is needed before a group is able to systematically impose on another group—whether in the form of warfare or in other ways. I think that, for a long time, Africa was in that condition, and that, as it proceeds away from that condition, African countries will be able to fight wars against one another. In a historical sense, though, that is an implication of advancement.
Kenneth N. Waltz, ‘Theory Talks #40: The Physiocrat Of International Politics’, 3 June 2011
Excuses In Our Sleep: Libya, the Arms Trade, Universities and the Political Economy of Human Rights
A common purpose Gains value as a common goal Let’s flail together If we must flail at all. Deep in the heart of the battle Caught in the switch of the flow Freedom from notes, she sells freedom from songs She sells freedom and arms Eritrea. I could have made these excuses in my sleep As if anyone had doubted them at all But if we arm Eritrea we won’t have to pay her And everyone can go home.
Future Of The Left, ‘Arming Eritrea’ (2009)
This now fairly-widely disseminated video of Saif Gaddafi brandishing his militarised manhood and promising death can only fuel the paroxysms of guilt and denial afflicting those previously enamoured of him. Not a topic to be neglected, fersure, and one that will be returned here at The Disorder Of Things soon (I promise). But there is another element at play, and one rather more materially linked to massacre and repression. Where are the guns coming from?
Last month, The Guardian engaged in one of its periodic moments of data-explication, borrowing somewhat from Dan O’Huiginn to set out which regimes get UK arms exports, and how much. Since David Cameron is unashamed in his claims that we’re merely helping democracies protect themselves (barring minor hiccups), the numbers and relations make interesting reading. The conventional (if perhaps flawed) metric for such political goods as freedom and democracy is that provided by Freedom House. The top five Middle East and North African beneficiaries of UK military export licences in 2009-2010 were Algeria (£270 million), Saudi Arabia (£64 million), Libya (almost £34 million), the United Arab Emirates (almost £16 million) and Jordan (£12 million).
Every single one is listed as ‘Not Free’ in the Freedom House Index for 2010.
Martin Luther King as an international thinker?

Monday 17 January marked the official US holiday honoring Martin Luther King, Jr. While watching Monday’s Democracy Now! program, featuring substantive excerpts from King’s speeches, the clarity with which he connected the domestic fight for equality to international politics, in particular poverty and war, struck me. The international aspects of King’s thinking, I believe, are important for two reasons.
King’s Radicalism
First, it challenges the interpretation of King as an insufficiently radical leader offered by some critics, and the co-option of King’s legacy not only by “moderate” liberals but also by conservative political figures in the US. King has become a symbol in the public consciousness of a safe reformism and a favorite icon for the type of liberal who abhors radicalism above any other political sin. As Michael Eric Dyson says, “Thus King becomes a convenient icon shaped in our own distorted political images. He is fashioned to deflect our fears and fulfill our fantasies. King has been made into a metaphor of our hunger for heroes who cheer us up more than they challenge or change us.”
A personal anecdote to illustrate the point: a couple of years ago while handing over the editorship of Millennium to the incoming editorial team, one of the new editors commented on the large poster of Che Guevara that hangs on the Millennium office door. The Che poster, so far as I know, predates most of us currently associated with the journal, therefore I suggested it should stay. I then asked why Che should go. My colleague suggested that Che’s participation in revolutionary violence made him an inappropriate icon – in many academic disciplines this might be a rather devastating point, but International Relations is full of characters far more violent and less admirable than Comrade Che – see Paul’s post on Kissinger, for example.

When asked who might better grace the walls of the office my colleague suggested Martin King or Mohandas Gandhi (a political figure subject to a similar post-hoc liberal deification), with their key qualification as acceptable iconography being that they had not participated in political violence. While I have a great deal of sympathy for non-violence, my own introduction to both King and Gandhi came through the study of non-violence political strategy, the liberal (and I think my colleague would gladly accept that identification) embrace of King or Gandhi, paired with the repudiation of Che, is (unintentionally?) disingenuous.
It’s a disingenuous embrace because it insists that the first rule of acceptable political action is a renunciation of physical violence, while at the same time turning a blind eye to the violence institutionalized in the state through everyday police brutality and legalized/legitimized imperial warfare, as well as the structural violence inherent to global capitalism. This misses the radical content of non-violence as practiced by King and obscures the link that exists between non-violent agitation and armed resistance. The political commitments and motivations of King and Che are remarkably similar, even as their fundamental orientations (Marxism vs. Christianity) and tactics (non-violent direct action vs. guerrilla insurgency) diverged. Continue reading
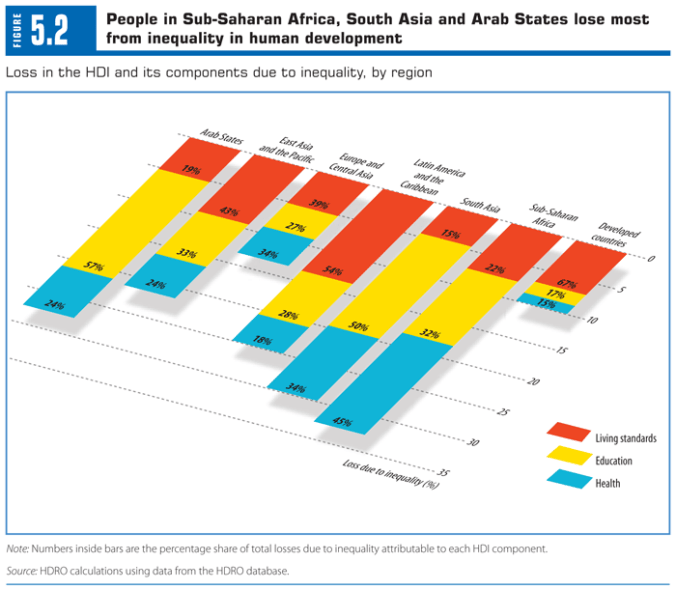
Inequality and the Human(e) Development Index
The UN Development Programme (UNDP) has for the last 20 years pioneered seemingly innovative approaches to development that have substantially redefined the terms on which development aid is conceived, offered and spent. The publishing of the first Human Development Report in 1990 was a bold move which made a case for measuring and judging countries’ developmental status in a way which focused on quality of life indicators as well as macro-economic statistics – an idea now which is completely mainstream and commonplace amongst donor governments and development practitioners. It also proposed the notion of ‘human security‘ in 1994; a subversive response to the ‘securitisation’ agenda emerging in the wake of the Cold War which sought to broaden both the referent of security and the range of relevant concerns. It was absolutely instrumental in pushing the Millennium Development Goals agenda – an incredibly ambitious and detailed set of targets for international development practice that served to underpin widespread agreement for the expansion of development funding across donor governments.
Its recent decision to measure inequality as a constituent part of development through its apparent role in determining the quality of life is, in this context, really interesting. On one level, it is indicative of the development community’s constant reflexivity – a term often used by David Williams – which recalibrates the tenor of its activities according to whatever the relevant crisis is supposed to be. Having been roundly critiqued and lambasted for the MDGs’ complicity with impoverishing neoliberal economic structures, we can read this ‘equality turn’ as the UNDP’s attempt to once more place itself on the vanguard of a more humane and responsive development agenda, moving itself away from the territory that the IFIs are starting to encroach upon.
It will be interesting to see whether and how the donors follow down this particular road. To a certain extent, the UNDP’s previous ‘innovations’ on human development, particularly with regard to adjusting for gender inequality, levels of absolute poverty and service provision, have all found various champions amongst western development agencies, all of whom have incorporated these issues seemingly deeply into their approaches to development, albeit perhaps through substantially de-radicalising the most substantive aspects of critique.
Inequality as an issue however poses a much more substantive threat to the international development agenda when pushed too far – not only does it cast doubt on the shining beaconof the self-made rich in the global South, but specifically, it starts to push against the foundational myth that ‘development abroad’ can be achieved with no corresponding change in the fortunes of ‘developed’ countries, a key threat to donor sanguinity and compliance with the UNDP’s more radical agendas. After all, if it is true within countries that vast inequalities impact on quality of life through skewing access to the goods that constitute human well-being, why would this also not be true between countries? The nonsense and yet widespread idea that some countries merely have to ‘catch up’ with others is belied by the inequality point but poses the much harder question for western countries and populaces to deal with: do I support international development enough to sacrifice any aspect of my own well-being?
As argued on an earlier post, the failure of highly-moralising development and anti-poverty agendas to deal at all with the central problem of inequality, both international and domestic, has been egregious and pervasive over the last 20 years, and looks to remain so in the future. The UNDP’s intervention is no doubt a timely one, although given the history of its more radical proposals, one which will probably be so watered down in practice as to be meaningless. Furthermore, by bringing this question within the competence of the ‘development’ policy specialists rather than engaging it as a public political question in ‘developing’ and ‘developed’ countries, the potential for getting to grips with the depth of this challenge seem remote.