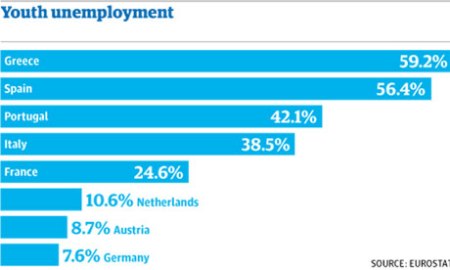
Ahoi, Disorders! We’re thrilled to host a guest post by Nicholas J. Kiersey, Assistant Professor at Ohio University, indefatigable student of Foucault, Italian Autonomism and Deleuze and Guattari, plus a die-hard fan of Battlestar Galactica. Nick is the author of papers on governmentality in Global Society, the biopolitics of the war on terror in New Political Science, everyday neoliberalism in the Journal of Critical Globalisation Studies, and is due to be published on the occupy movement and affective labour in the financial crisis in Global Discourse and Global Society respectively. Oh, and he’s also Irish. That’s also important. Below is Nick’s review of Dave Eden’s new book on Autonomist thought, which one can only hope has not gone entirely unnoticed because it’s one of the finest on the subject!
Ahoi, Disorders! We’re thrilled to host a guest post by Nicholas J. Kiersey, Assistant Professor at Ohio University, indefatigable student of Foucault, Italian Autonomism and Deleuze and Guattari, plus a die-hard fan of Battlestar Galactica. Nick is the author of papers on governmentality in Global Society, the biopolitics of the war on terror in New Political Science, everyday neoliberalism in the Journal of Critical Globalisation Studies, and is due to be published on the occupy movement and affective labour in the financial crisis in Global Discourse and Global Society respectively. Oh, and he’s also Irish. That’s also important. Below is Nick’s review of Dave Eden’s new book on Autonomist thought, which one can only hope has not gone entirely unnoticed because it’s one of the finest on the subject!
All quotes in the below are to Eden’s text, unless otherwise stated.
No doubt, a return to the commodity is a risky venture. As Dave Eden puts it in his exceptional new book, certain framings of the power of the commodity can lead to an embrace of austerity, a “romanticization of poverty” or, worse, “a reactionary anti-capitalism”. Nevertheless, he asserts, a return to the commodity may ultimately be required. Currently popular framings of social movements, such as those of Hardt and Negri, he notes (citing Franco Berardi), offer very bright and “jolly” interpretations of the possibilities of the age, pretty much ignoring the need for a critique of the commodity form altogether. As such, they appear to have little sense of what it is that keeps capitalism going, or what it is that might finally send it on its way! However, while Eden wishes to convince us that we cannot do without the critique of the commodity, it is unclear if he ultimately achieves this goal. For his argument stands or falls on his ability to convince us that it is possible both to embrace this critique and remain faithful to an internal theory of capitalist power. This is a difficult circle to square and, by the end of the book, Eden seems to have done little to address it – an irony given that this is actually one of the areas where the targets of his critique are especially strong.
At the heart of Eden’s explanation of Autonomism, its virtues and its flaws, is the “Copernican inversion” of Marxism in which Mario Tronti asserts that the true dynamic force behind capitalism’s development is the workers rather than capital. Starting from this core observation, Eden proceeds to offer a survey and critque of Tronti’s heirs, particularly Antonio Negri. For Negri, the current order in world power is defined most completely by the antagonism between ‘Empire’ and the ‘multitude,’ where the latter term endeavors to expand the definition of the proletariat in order to capture not only the vitality of “labour as a whole” but to encompass the full diversity of the identities which compose it, and Empire is the power which dominates the multitude. Breaking with traditional Marxism, however, Empire is not capitalism. Rather, it is a multi-valent regime which proscribes democracy in order to bolster a global order of things which is capitalist, statist, racist, and gendered, among other things. Challenging this power, however, the Multitude realises the creative possibilities of today’s intellectual and affectively efficacious labour, and incorporates them in its struggle for self-actualisation.